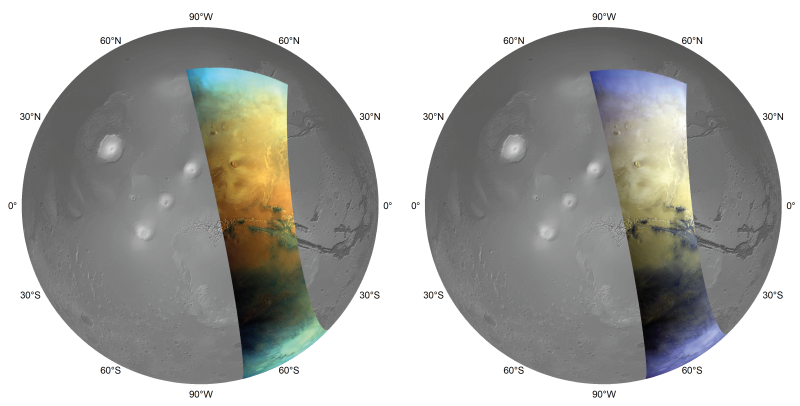
It was launched in 2003 and orbits the red planet. Mars Express celebrates twenty years of observing Marsreleasing a full-colour global mosaic detailing minerals, the composition and circulation of the atmosphere, peering beneath the crust and highlighting the various phenomena that interact in the Martian environment.
Consisting of ninety images taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC), the mosaic provides information about the composition of Mars for regions extending up to 2500 km Taken from heights incl Between 4,000 and 10,000 kilometers. The group has produced a global, full color rendition of Mars.
Known for its reddish color due to high levels of oxidized iron, Mars appears dark and blue in these images. around Gray-black basalt sand of volcanic origin Which form dark layers of sand, where it accumulates and moves in the wind, creating huge sand dunes inside the impact craters.
Materials exposed to water tend to appear lighter: the most common water-altered mineral on Marspride and the sulfate, which looks particularly bright on the reference color palette. For these images micro was used Omega Spectrometer.
Even if indirectly, these minerals are a “smoke gun” that confirms thatwaterfall liquid It has been present on Mars for a long time, altering rocks over time to form important mud deposits such as Mawrth Vallis.
Valles Marineris Valley with surface details annotated: sulfate deposits, haze, haze and cloud cover. This tectonic feature extends more than 4,000 km from east to west and up to 700 km from north to south, and is the largest and most beautiful canyon system in the solar system.
ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/G. Michael, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The sulfate minerals are shown in the adjacent image and appear covered with a thin layer of patina sand dark. Unlike clay deposits, sulfate minerals indicate more acidic environmental conditions that would be less suitable for life.
To create the color mosaic, thanks to HRSC’s nine imaging channels, the team had to considerOpacity effect, due to the continuous evolution of the Martian atmosphere, making it difficult to accurately determine surface colors from orbit. Dust spreads and reflects light, causing colors to transfer between images.
The “noise” effect was overcome during image processing, reducing color contrasts between different parts of Mars: each image indicates a color model derived from high-altitude observations.
This arrangement allowed the HRSC team to preserve color differences and detect A Color vision of Mars richer than ever.
the mission Mars Express by Esa It also sees the sharing of a long line of Italian expertise, coordinated by the Italian Space Agency: lo Pfs Fourier spectrometer To study the atmosphere and rBeneath the roof he ran Marcis Mars Advanced Radar for Sounding the Subsurface Ionosphere, achieved with the contribution of Jpl from NASA.
The machine is also Italian Fenir, which consists of the Omega spectrometer and the electronics of the Aspera Neutral Imager. Also in the HD stereo camera team hrsc There are Italian scientists.
Opening: Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin/MOLA Science Team, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO

“Infuriatingly humble social media buff. Twitter advocate. Writer. Internet nerd.”