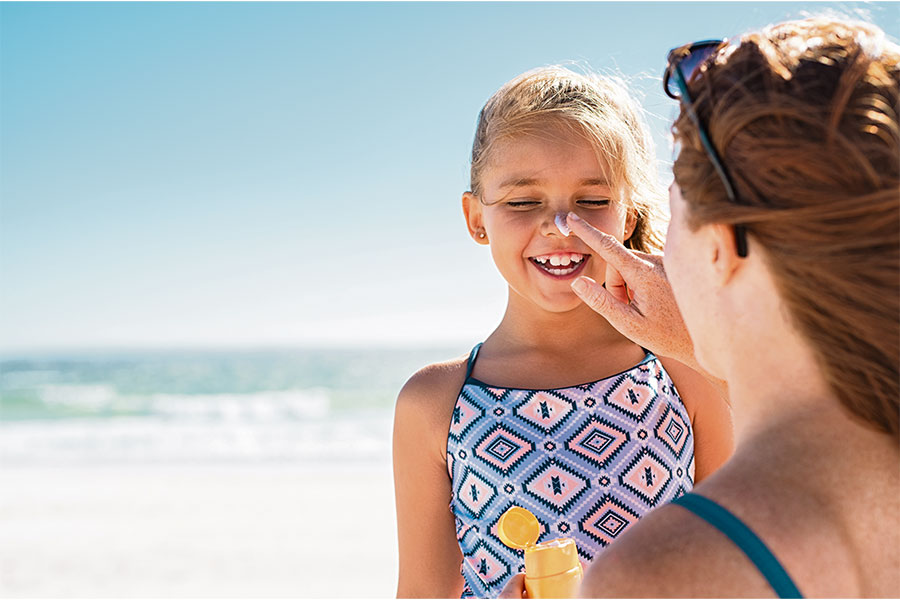
Photoprotectors are chemical substances that, when applied to the skin, reduce the harmful effects of sunlight. The offer of photoprotectors is numerous: creams, milks, lotions, gels, sprays, lipsticks and make-up, which means that there is a type of photoprotector for every skin type.
Image protection rules
In order to carry out the correct photoprotection, you must know the person’s phototype and the expected solar radiation index. The role of photoprotectors should not be overestimated, and their use should be accompanied by other photoprotective measures:
- Between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m., you should not be exposed to the sun, not even with sunscreen.
- It is best to be indoors or in the shade. At the beach, it is not useful to be under an umbrella, as the sand reflects a lot of sunlight, which reaches the skin indirectly.
- Walking or being in water does not protect.
- If it is cloudy, 70-80% of UV rays reach the skin.
- If exposure to sunlight is unavoidable, appropriate clothing and sunscreen should be used.
- In snow, the reflection of sunlight increases, and its effects are doubled.
- The first and second phototypes should never attempt tanning, because they will fail, and will always burn.
- The first periods of exposure to the sun should be gradual: 10, 15, 20 minutes, preferably while moving, and never more than 30 minutes per day.
- Precautions should be taken in the most sensitive areas of the body: face, lips, neck, head, chest, breasts and ears.
- Products containing alcohol should not be used before sun exposure, as they can cause dark spots on the skin.
- You should drink plenty of fluids to compensate for water loss through sweat.
- After sunbathing, a person should shower with soap and water, without a lot of perfume or surfactants (the skin is damaged by air, dryness, chlorine or salt). Then apply a moisturizing cream that nourishes, refreshes and moisturizes the skin.
- In order to prevent skin aging, it is recommended to consume a sufficient amount of fresh fruits, vegetables and grains that contain a high level of fiber and antioxidants.
- Sunscreen should be applied every 30-60 minutes, or more often if you sweat a lot.
It should be borne in mind that the most effective against UV rays are clothing. The most suitable is cotton, not porous and very dry (wet clothes stick to the skin, the air layer there is removed, so the ability of clothes to filter out solar radiation is significantly reduced or lost). Eyes should be protected with sunglasses that absorb UV rays.
Negative health effects resulting from exposure to sunlight
The sun is essential for life and has many beneficial effects on the body. In humans, it stimulates the formation of vitamins A and D, which contribute to the formation and strengthening of bones and teeth.
But excessive exposure to sunlight can become very harmful to human skin: skin cancer, premature skin aging, cataracts and other eye diseases.
The direct negative effects are:
- Sunburn – First there is erythema, which begins within a few hours of starting exposure to sunlight and reaches its maximum extent within 12-24 hours. If exposure is too long, inflammation, edema and blisters can occur.
- Tanning – People with highly photogenic skin tanning immediately, without developing erythema first. Tanning is the result of the action of ultraviolet rays
Tanning only protects against burns, but does not protect against late effects associated with exposure, such as aging or the development of skin cancers. Melanin protects against UVA, but not UVA, radiation thus reaches the deeper layers of the skin, where it causes ectasia of blood vessels in the dermis, collagen degeneration and skin carcinogenesis. The cumulative effects of UVA and its internal action appear over time, when prevention is not possible.
- Changes in the immune system
- sunstroke
Late negative effects are:
- Photoaging of the skin (wrinkles, spots, etc.) – UV rays cause the formation of free radicals with a high oxidizing capacity, which damage cells and cause aging of the skin, which loses its elasticity, becomes rougher and spots appear.
- The appearance of skin tumors
- Eye changes – The exposure of the eye to UV rays depends on many factors: radiation reflected from the ground, the intensity of light from the sky, the amount of light reflected from the atmosphere or the use of sunglasses UV rays can cause reversible disorders, such as photokeratitis or conjunctivitis Optical.
Chronic effects it can cause include pterygium (white, opaque tissue that forms on the cornea), squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva and cataracts.
We must not forget
- The sun accumulates and the skin “remembers” all the radiation it has received since childhood. The negative effects that appear on the skin are the result of the total amount of solar radiation it receives over the years.
- It has been proven that a major risk factor for skin cancer is exposure to recurrent sunburn or burns in childhood and adolescence.
- Continuous exposure to the sun’s rays (people working outdoors) is no less dangerous than intermittent but intense exposure (at the beach).
- If any skin spot that changes shape or color is detected, it should be consulted quickly, as the skin cancer detected can be treated in time.
- Light protection tools are not the primary and final preventive measures, because they do not provide complete protection on their own, and their use should not be the only one, but should be included with other protective measures.

“Infuriatingly humble social media buff. Twitter advocate. Writer. Internet nerd.”