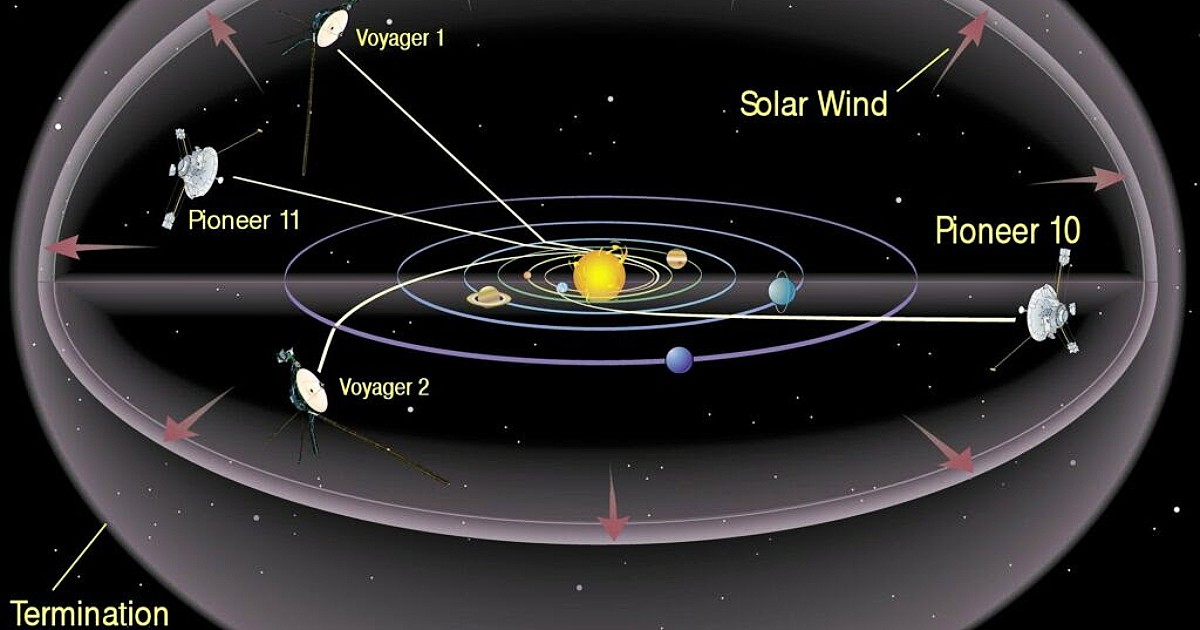
The Voyager sensors They raised disturbing scientific questions as they moved away from the solar system. Now, scholars Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) has come up with a concept for the interstellar probe (IP), $3.1 billion is important To capture the scientific challenge launched by the Voyager probe a decade ago after leaving the heliosphere, the Sun’s influence zone. Few of the Voyager probes expected them to survive long, and yet their fascinating observations still came in, they overturned many beliefs about the outer limits of the solar system. The Voyager data are so perplexing that some prominent researchers have said that the probes may not have reached interstellar space yet, possibly because the heliosphere extends farther than previously thought.
He said, “The only way to see what our aquarium looks like is to stand outside and look inside.” Ralph McNutwho worked on the plasma detector for the Voyager mission, NASA’s epic mission on the outer planets He started in 1977. Now, McNutt needs to convince a jury of his colleagues to get the funding needed to get the job started. His team presented an interstellar probe concept study for the Decadal Survey of Solar and Space Physics, a community exercise led by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine that will prioritize the field over the next 10 years. The committee is expected to begin deliberations next month and deliver its verdict in 2024. An admiration for intellectual property would go a long way in securing NASA support For a probe, ideally, that would take off in 2036.
In 2007, Voyager 2 provided a big surprise when it dived below the plane of the ecliptic, the plane at which the planets of the solar system orbit. go through what’s calledTermination shock‘, where the solar wind begins to falter when it is hit by gases and interstellar dust through which the solar system passes on its journey inside the galaxy. Voyager 1 went through ‘termination shock’ 3 years ago, about 94 astronomical units (AUs) from Earth, where there is 1 astronomical unit The average distance between the Earth and the Sun, that is about 150 million km. However, his plasma detector failed by 1980 during his visit to SaturnSo he could not measure the deceleration of the solar wind. Models expected wind speeds to slow from 1.2 million kilometers per hour to about 300,000 kilometers per hour, but Voyager 2 recorded wind speeds of 540 thousand kilometers per hour. A symbol of how little has been explored and understood about space outside the solar system. Chinese scientists are planning a similar mission called Interstellar Express, which can be launched at approximately the same time. “buckle up,” encouraged Jim Bell, a planetary scientist at Arizona State University, Tempe, and former president of the Planetary Society. “It’s a space race to the edge of the solar system!”
Alessandro Berlingeri
Support ilfattoquotidiano.it
We really need
of helping you.
For us the only gentlemen are the readers.
But those who follow us should contribute because, like everyone else, we don’t work for free. Be supportive too.
click here
Thank you
Previous article
Lung cancer can be caused by pollution in non-smokers. Scientists: “Climate health is linked to human health”


“Unable to type with boxing gloves on. Freelance organizer. Avid analyst. Friendly troublemaker. Bacon junkie.”